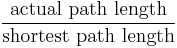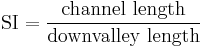Sinuosity
Sinuosity or sinuosity index is a measure of deviation of a path between two points from the shortest possible path (the geodesic, in planar geometries a straight line between the two points). It is given by the ratio of:
This sinuosity index is 1 in the case in which the actual path length is equal to the shortest path length, and can increase to infinity for a closed loop (where the shortest path length is zero) or for an infinitely-long actual path.[1]
Rivers
In studies of rivers, the sinuosity index is similar but not identical to the general form given above, being given by:
The difference from the general form happens because the downvalley path is not perfectly straight. The sinuosity index can be explained, then, as the deviations from a path defined by the direction of maximum downslope. For this reason, bedrock streams that flow directly downslope have a sinuosity index of 1, and meandering streams have a sinuosity index that is greater than 1.[2]
References
- ^ Leopold, Luna B., Wolman, M.G., and Miller, J.P., 1964, Fluvial Processes in Geomorphology, San Francisco, W.H. Freeman and Co., 522p.
- ^ Mueller, Jerry (1968). "An Introduction to the Hydraulic and Topographic Sinuosity Indexes1". Annals of the Association of American Geographers 58 (2): 371. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8306.1968.tb00650.x.